Products
KESS (Kinetic Energy Storage Systems)
KESS
KESS Kinetic Energy Storage Systems (Flywheels)
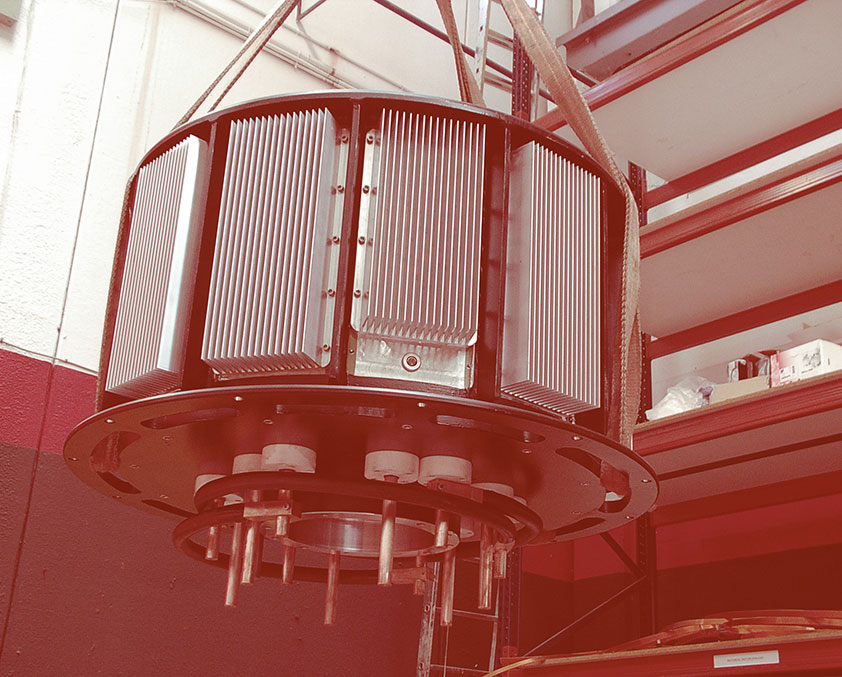
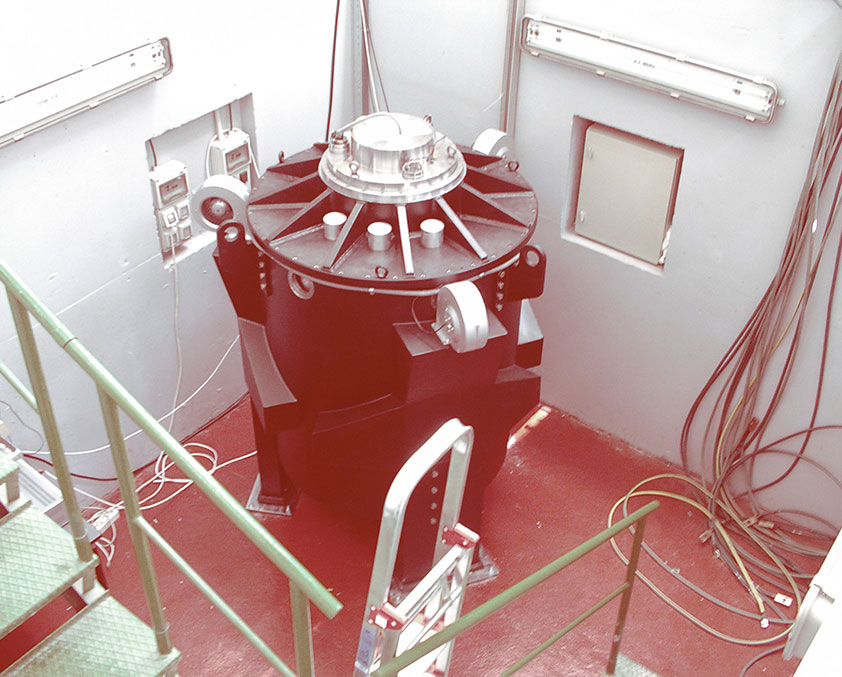
Kinetic Energy Storage Systems (KESS) are based on an electrical machine joined to a Flywheel. When the system stores energy, the electrical machine works as a motor and the flywheel is accelerated until it stores the nominal energy. When the system provides energy, the electrical machine works as a generator and the flywheel decelerates. KESS transform electrical energy into kinetic energy or kinetic energy into electrical energy. The aim is to store electrical energy when it is not used by other devices and to provide those devices with electrical energy when they need it.
ELYTT ENERGY designs and manufactures advanced Flywheels Energy Storage Systems that provide ride-through power and voltage stabilization for power quality and power recycling applications.
Our Flywheel products are:
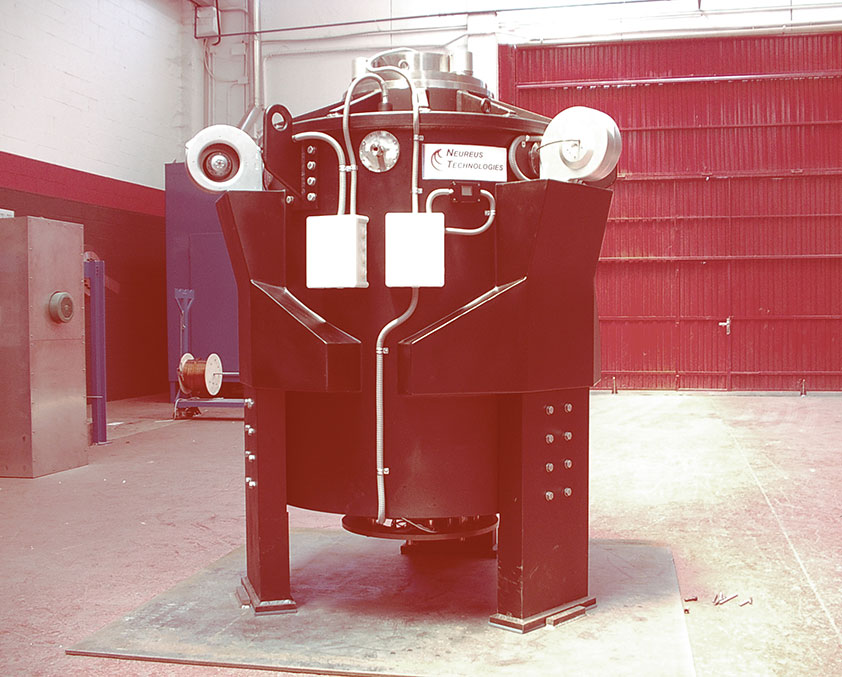
Flywheel100kW
Specifications
| PARAMETERS | VALUE | UNITS |
|---|---|---|
| Energy | 5 | MJ |
| Power | 200 | kVA |
| Operation Voltage | 1.100 | V |
| Current max. | 257 | A |
| Number of phases | 3 | |
| Rotating speed | 9.000 | r.p.m |
| Flywheel diameter | 830 | mm |
| Rotating mass weight | 250 | kg |
| Total weight | 1.000 | kg |
| Guiding system | Standard Bearings with magnetic levitation | |
| Operation conditions inside | Partial vacuum |
Flywheel400kW
Specifications
| PARAMETERS | VALUE | UNITS |
|---|---|---|
| Energy | 200 | MJ |
| Power | 500 | kVA |
| Operation Voltage | 1100 | V |
| Current max. | 257 | A |
| Number of phases | 3 | |
| Rotating speed | 6.600 | r.p.m |
| Flywheel diameter | 1.100 | mm |
| Rotating mass weight | 6.000 | kg |
| Total weight | 10.000 | kg |
| Guiding system | Standard Bearings with magnetic levitation | |
| Operation conditions inside | Partial vacuum |
Flywheels on board
The Flywheel on board alternative is to store the braking energy on the train. This not only avoids the electrical complications of regenerating through the traction power supply network. It reduces the rated power requirement of that network by lopping demand peaks during acceleration, saves energy by reducing losses in the catenary or conductor rail, and by limiting voltage drop it allows substations to be further apart.
Tram on board TECHNICAL DATA
Electrical Data
Power: 310 kW
Stored Energy: 2.77 kWh
Energy at Full Power: 1.87 kWh
Time at Full Power: 34 seconds.
Output Voltage: from 400 V to 1100 V
Input Voltage: from 450 V to 1100 V
Mechanical Data
Speed: from 5028 rpm to 10067 rpm
Weight: 1500 kg
Dimensions (machine)
Height: 750 mm
Diameter (Footprint): 934 mm.
Dimensions (electronics)
Height: 750mm
Width: 1600 mm
Depth: 2104 mm
Environmental Data
Operating temperature: from -20∫C to 40 ∫C
Humidity: 95 %
Noise: 70 dB to 1mf
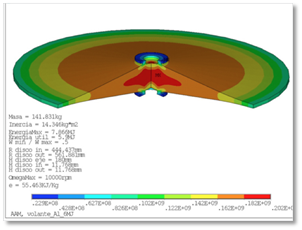

Specifications
| PARAMETERS | VALUE | UNITS |
|---|---|---|
| Energy | 5 | MJ |
| Power | 200 | kVA |
| Operation Voltage | 1100 | V |
| Current max. | 257 | A |
| Number of phases | 3 | |
| Rotating speed | 9000 | r.p.m |
| Flywheel diameter | 830 | mm |
| Rotating mass weight | 250 | kg |
| Total weight | 1000 | kg |
| Guiding system | Standard Bearings with magnetic levitation | |
| Operation conditions inside | Partial vacuum |
Kinetic Energy Storage Systems (KESS) transform electrical energy into kinetic energy or kinetic energy into electrical energy. The aim is to store electrical energy when it is not used by other devices and to provide those devices with electrical energy when they need it.
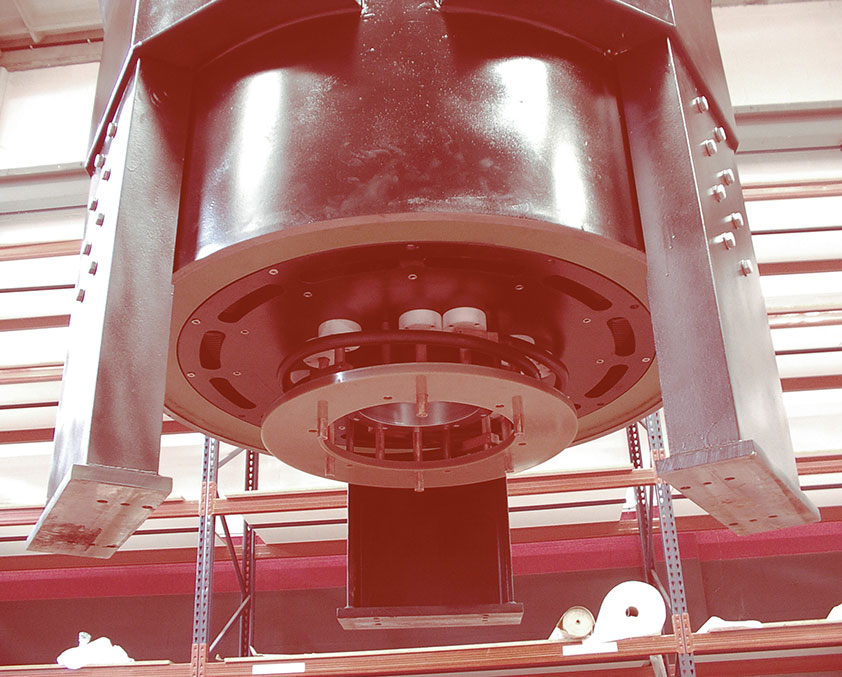
Our Flywheels are basically composed by a flywheel with a reluctance electrical machine attached.
The electrical machine transforms energy bidirectionally, that means, when the electrical machine works as motor, it absorbs electrical energy from the net to transform it into kinetic energy. When the electrical machine works as generator, it transforms the stored kinetic energy into electrical energy, providing to the connected devices such energy.
If you wish more information about Flywheel technology and applications, please visit the following link: